Kitchen Science: Cabbage Chemistry
ResourcesWatch this short video to learn how to conduct your own cabbage experiment to learn about acids and alkalines.
Items you'll need:
- Red cabbage
- Lemon juice
- Toothpaste
- Water
- Bicarbonate of soda
- Vinegar
- Set of glasses
Science behind the experiment
Some chemicals change colour as they react with other things and this is the principle behind cabbage chemistry.
The pigment that gives red cabbage its colour is called anthocyanin and just so happens to be a chemical that changes colour, this is our indicator. This means that as you change the pH (level of acidity), it will change colour accordingly.
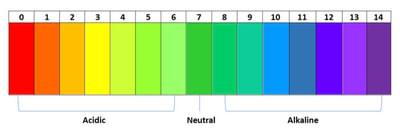
The pH scale is a measure of how many free protons are in a solution. A strong acid (pH1) is a chemical that donates lots of protons while a strong base (pH14) is a chemical that accepts lots of protons. Pure water is neutral and donates and accepts electrons equally.
In a strongly acidic environment, when there are lots of protons, the anthocyanin molecule will take on lots of these protons and become a pink/ red colour. At the other extreme, in a very basic (alkaline) environment, the anthocyanin will effectively be stripped of its protons completely and be a completely different colour.
By mixing the red cabbage solution with different household chemicals, we can test how acidic or basic they are by comparing the colour of the resulting solution against a standard chart.
Some people might ask why measuring pH is important and the main reason is safety. All solutions have a pH and if they are coming into contact with people (e.g. drinks, cosmetics) this must be fairly neutral, or it will hurt you.
Key Terms
- Anthocyanin – Anthocyanins are the pigments that give the attractive red, blue, purple, violet, and intermediate red-purple to berries and many other fruits, vegetables, and grains.
- pH – pH is a scale used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. The scale ranges from zero (acids) to 14 (alkalis), with seven as a neutral middle.
- Indicator - An indicator is a substance that changes colour when it is added to acidic or alkaline solutions.
- Protons – a proton is a subatomic particle found in the nucleus of every atom. It has a positive electrical charge, equal and opposite to that of the electron.
Activities and Questions
Try and test out other things you can find in your kitchen cupboards, can you make an entire pH scale?
What happens if you mix one of your cups containing an acid with another containing an alkali?
Change your indicator. Swap red cabbage for beetroot.